Comprehensive Guide to Maize Weevil Control for Farmers and Agribusinesses
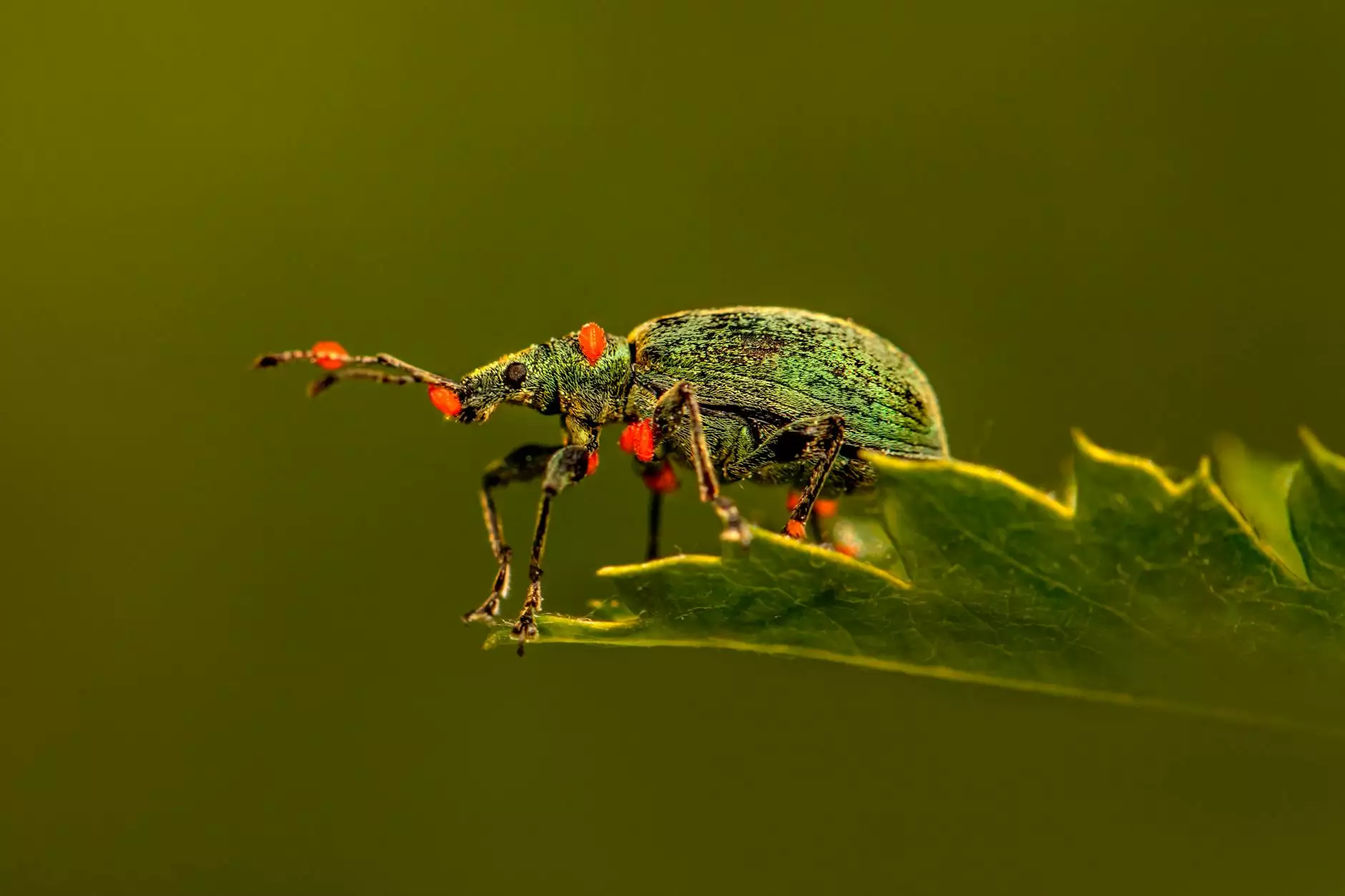

In the realm of modern agriculture, maize weevil control is a critical aspect that directly impacts crop yield, storage quality, and overall farm profitability. These tiny pests, scientifically known as Sitophilus zeamais, pose a significant threat to stored grains and can lead to devastating economic losses if not managed effectively. This comprehensive guide explores effective strategies, innovative solutions, and best practices to combat maize weevils, ensuring your farm remains productive and your stored grains remain pest-free.
Understanding the Menace: What is Maize Weevil?
The maize weevil is a small, brownish beetle, commonly found in tropical and subtropical regions worldwide. It primarily infests stored maize and other grains, where it reproduces rapidly under favorable conditions. The lifecycle of the maize weevil involves four distinct stages: egg, larva, pupa, and adult, with the entire cycle often completing within a few weeks.
Adult maize weevils lay their eggs inside the grains, and the emerging larvae feed inside, damaging the kernel's structure. This feeding not only reduces the weight and quality of the grain but also promotes mold growth and further pest infestation.
The Economic Impact of Maize Weevils on Agriculture
Economic losses attributed to maize weevils are substantial, especially in regions where farmers rely heavily on stored grains for sustenance and sale. Infestation can lead to:
- Reduction in grain weight and nutritional value
- Increased wastage due to mold and rot
- Higher costs associated with pest control measures
- Potential rejection of stored grain in markets
- Decrease in farm income and profitability
Therefore, implementing effective maize weevil control strategies is essential for safeguarding economic stability and ensuring food security in farming communities.
Factors Favoring Maize Weevil Infestation
Understanding the environmental and farming factors that favor maize weevil proliferation helps in developing targeted control measures:
- Temperature and humidity: Warm and humid conditions accelerate weevil reproduction and activity.
- Storage practices: Poorly sealed storage facilities provide easy access and promote infestation.
- Initial grain quality: Damaged or already infested grains promote rapid spread.
- Crop residues and weeds: Presence of leftover grains and weeds can serve as breeding grounds.
Proactive Prevention Strategies for Maize Weevil Control
Prevention remains the most effective method to combat maize weevil infestation. Implementing strict preventive measures can significantly reduce the risk of outbreaks:
1. Selecting Proper Grain Quality
Start with high-quality, pest-free grains. Ensure that grains are fully mature and free from damage or existing pests before storage.
2. Effective Cleaning and Drying
Thoroughly clean storage facilities and drying areas to remove residual grains, debris, and pests. Proper drying of grains to a moisture content below 13% inhibits weevil development.
3. Use of Suitable Containers and Storage Facilities
Utilize airtight, pest-proof storage containers made of metal, plastic, or other sealed materials. Keep storage facilities clean, well-ventilated, and elevated to prevent access by pests.
4. Application of Natural and Chemical Repellents
Utilize natural repellents like neem leaves and diatomaceous earth, which are eco-friendly and proven effective against maize weevils. Chemical protectants should be used with caution and following safety protocols.
5. Regular Inspection and Monitoring
Implement regular pest monitoring practices, including the use of pheromone traps and inspection for signs of infestation. Early detection allows for prompt intervention.
Effective Maize Weevil Control Methods
Once prevention measures are in place, various control methods can be employed to handle existing infestations. Combining these methods enhances pest management efficacy and promotes sustainable farming practices.
1. Mechanical Control Techniques
Mechanical control involves physical removal of infested grains and pests. Techniques include:
- Sorting and discarding heavily infested grains
- Sieving to remove adult weevils and larvae from stored grains
- Use of insect traps to catch adult maize weevils
Mechanical methods are environmentally safe but require diligent monitoring and repeated application for lasting results.
2. Biological Control Strategies
Biological control offers a sustainable alternative by utilizing natural predators or pathogens to suppress maize weevil populations:
- Predatory beetles: Certain species predate on maize weevils and larvae, providing biological pest suppression.
- Entomopathogenic fungi: Fungi like Beauveria bassiana infect and kill maize weevils, offering an eco-friendly control option.
Incorporating biological control agents into pest management programs promotes long-term control with minimal environmental impact.
3. Chemical Control Options
Chemical pesticides should be used judiciously, adhering to safety guidelines and local regulations. Commonly used chemicals include phosphine and methyl bromide, but these require careful handling due to health and environmental risks. Integrated pest management (IPM) emphasizes minimal chemical intervention, reserving such options for severe infestations under expert guidance.
4. Innovative Technologies in Maize Weevil Management
Advances in agricultural technology have introduced new tools and techniques for maize weevil control:
- Temperature treatment: Heating grains to specific temperatures can eliminate weevils without damaging the crop.
- Hermetic storage: Airtight storage systems that create an oxygen-depleted environment, suffocating the pests and preventing infestation.
- Smart monitoring sensors: IoT devices that monitor temperature, humidity, and pest activity, enabling real-time pest management decisions.
Best Practices for Sustainable Maize Weevil Management
Sustainable pest management aligns with eco-friendly practices, safeguarding both the environment and farm profitability. Here are key best practices:
- Implement crop rotation and diversification to break pest life cycles.
- Maintain cleanliness in storage facilities to deter pest establishment.
- Use resistant maize varieties where available.
- Employ integrated control methods combining mechanical, biological, and chemical techniques.
- Educate farm staff on pest identification and management protocols.
Partnering with Industry Leaders in Pest and Farm Equipment Management
For effective maize weevil control, collaboration with experienced industry providers like TSGC Inc. ensures access to state-of-the-art equipment, pest prevention products, and farm maintenance solutions. Their expertise in Farm Equipment Repair and Farming Equipment strengthens the farm's capacity to implement comprehensive pest management and maintain optimal storage conditions.
Conclusion: Embracing the Future of Maize Weevil Control
Effective maize weevil control is a multifaceted challenge that demands a proactive, informed, and integrated approach. Preventive measures, innovative technology, environmentally friendly control methods, and industry partnerships are pivotal in safeguarding your crops and storage systems. Embracing these strategies not only enhances crop security but also promotes sustainable farming practices, ensuring profitability and food security for years to come.
By staying vigilant and adopting best practices, farmers can drastically reduce maize weevil infestations, contribute to sustainable agriculture, and elevate their productivity to new heights. Remember, early detection, combined with integrated pest management, is the key to victory against maize weevils.